Inter Function communication
The calling and called functions are two different entities and they need to communicate to exchange data. The data flow between the calling and the called functions can be divided in to three strategies: a downward flow, an upward flow and a bi-directional flow.
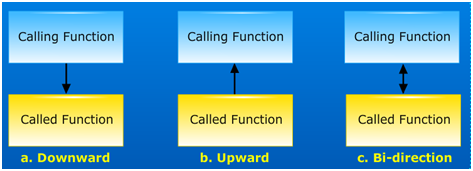
Note: The C language uses only pass by value and returns to achieve three types of communications between a calling and a called function.
Downward communication:
In downward communication, the calling function sends data to the called function. The called function may change the value passed, but the original values in the calling function remains in the same. An example of this type of communication is passing data to a print function.
int main(void)
{
int a;
.....
downFun (a,15);
...
} // main
void downFun (int x, int y)
{
...
return;
} //downfun
//Function Declaration
void downfun (int x, int y)
int main(void)
{
// Local Definitions
int a=5;
// Statements
downFun (a,15);
printf(“%d\n”, a);
return 0;
} //main
void downFun(int x, int y)
{
//Statements
x = x+y;
return;
} //downFun