Arrays in C Programming
Arrays are a collection of homogeneous data items stored under a unique name. The values in an array are called elements of an array. These elements are accessed by numbers called, ‘subscripts of index numbers’, as shown earlier. Arrays may be of any data type.
In the previous example, it has been shown that the ten variables are initialized first, then the variables are read and displayed in the output.
Arrays are of two types:
One/Single dimensional array
Multi-dimensional array
Declaration and Definition
For example: The scores array.
The ‘scores’ is the name of an array, elements are the 9 scores and indexes are the numbers assigned to each score (0-8).
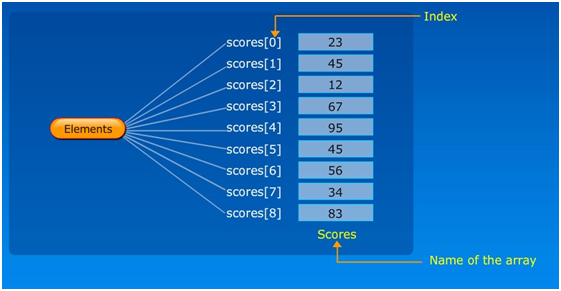
Declaring and defining the scores array.
Syntax:
<data-type> <name of elements> [<array size>]
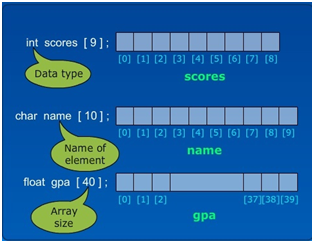
The array size must be an integer constant, which is greater than zero. The type of elements can be any C data type.
The array size is indicated in square brackets ‘[]’.
Note:
Only fixed-length arrays can be initialized when they are declared.
Variable length arrays must initialized during run time by, assigning values.
Initializing Arrays
The initialization of an array in C program can be either one at a time or by using a single statement.
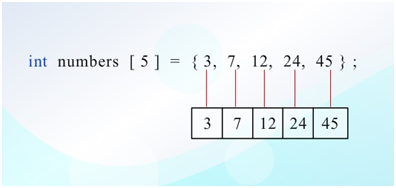
Single statement of fixed length array
Variable length array (initialization without size)
Partial initialization of an array
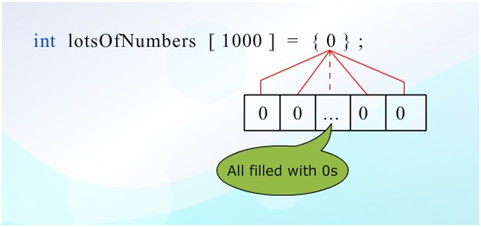
Initialization to all zeros
Single statement of fixed length array
Variable length array (initialization without size)
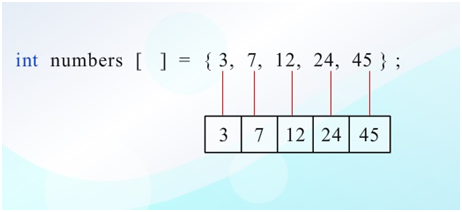
Partial initialization of an array
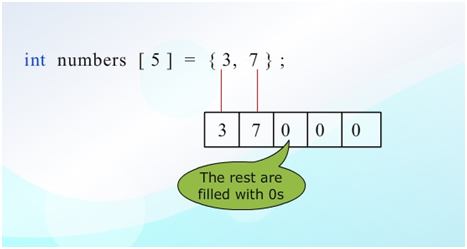
Initialization to all zeros