BASIC BEHAVIORAL MODELING II
Use Cases
- Names
- Actors
- Flows of Events
- Scenarios
- Collaborations
- Organizing Use Cases
- Common Modeling Techniques
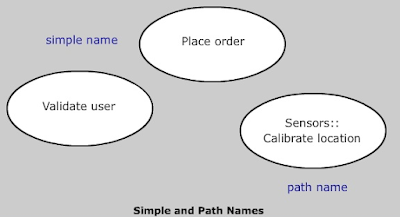
Names:
Every use case must have a name to distinguish itself from other use cases such as the simple name and path name
Actors:
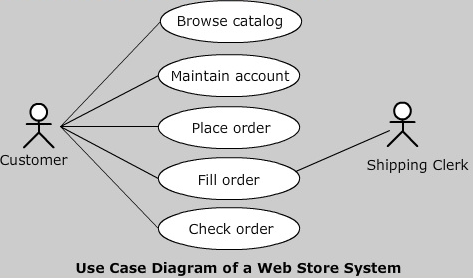
- It represents a systematic set of the roles the users play while interacting with the use cases
- An actor exhibits a role when a human, a hardware device, or even if another system plays with a system
- Actors and use cases are connected by association
Flows of Control:
- It includes how and when the use case starts and ends
- It also includes when the use case interacts with the actors and what objects are exchanged, and the basic flow and alternative flows of the behavior
- The behavior of a use case can be specified by describing a flow of events in text
- There can be main flow of events and one or more exceptional flow of events
Example:
- This use case begins when a customer arrives at a store's register checkout with items to purchase
- The cashier starts a new sale with the register
- The system creates a new sale with the register
- The cashier records the identifier and quantity for each LineItem
- The system determines description and price of the current item from the product catalogue and adds the item to the running sale. The details and subtotal are displayed
- On completion of items entry, the cashier indicates to the POST that the sale is complete
- The system computes the total including the applicable taxes and displays the information
- To make a payment, the cashier records the 'cash received' amount
- The system shows the balance due, records the payment and generates a receipt
- The customer leaves with the items purchased
- A scenario is a specific sequence of actions that illustrates behavior in a particular condition
- For each use case, there will be primary scenarios and secondary scenarios
- For example, when you buy some items at point-of-sale terminal, paying by cash, paying by credit card, paying by cheque are all different scenarios
Collaborations:
Collaborations are society of classes and other elements that work together to implement the behavior of use cases.

Optimizing Use Cases:
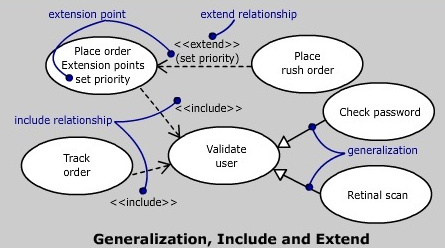
- Grouping them in packages
- Specifying generalization, include, and extend relationships among them
Generalization:
- The child use case inherits the behavior and meaning of the parent and usual adds/overrides the behavior
Include relationship:
- Base use case explicitly incorporates the behavior of another use case at a location specified in the base.
- Shown as a dependency, stereotyped as include
Extend relationship:
- Base use case implicitly incorporates the behavior of another use case at a location specified indirectly by the extending use case
- Rendered as a dependency, stereotyped as extend
Post a Comment
Post a Comment